blood_p <- read.csv("../data/WilcoxonSignedRank_TTR.csv", dec = ".")R vs SAS vs StatXact - Wilcoxon signed-rank test
Wilcoxon signed-rank test in R, SAS and StatXact
Introduction
This section compares the implementation of Wilcoxon signed-rank test in R, SAS and StatXact.
General Comparison Table
The following table provides an overview of the methods support comparability between R, SAS and StatXact for the new analysis point.
| Analysis | Supported in R | Supported in SAS | Supported in StatXact | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wilcoxon signed-rank test with p value only | YES | YES | YES | Available in all, but results match only between R and StatXact. See details on p value on each software page. |
| Hodges-Lehmann estimator | YES | NO | YES | Available in R and StatXact only. In SAS needs to be derived manually. |
Exact/non-exact method Non-exact method with/without continuity correction |
YES YES |
NO NO |
YES NO |
Stats package in R and StatXact support both options. SAS applies a default one depending on N. Only Stats package in R support both options. |
| Dataset with “0” differences | YES | NO | YES | SAS ignores 0s. In R only Coin package supports. |
| Dataset with ties | YES | YES | YES | Supported in SAS and StatXact. In R only in Coin. |
Example Data
Analysis will be conducted on the example of anonymized data from 2-period, cross-over study comparing treatments A and B in patients with asthma and acute airway obstruction induced by repeated mannitol challenges.
For the purpose of the results comparison we will consider a specific case where the dataset has no ties and N (number of observations) = 240.
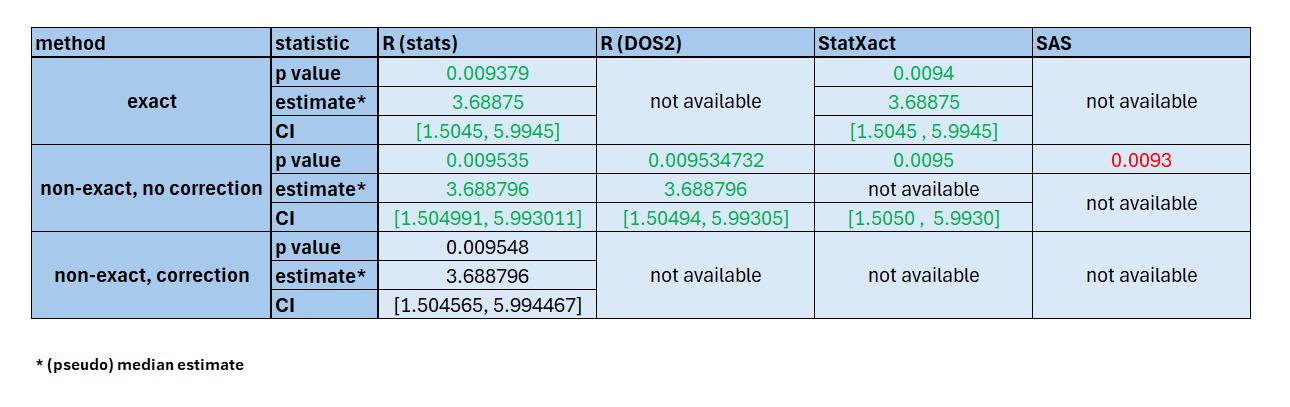
Wilcoxon signed rank test was applied to analyse the time to return to baseline FEV1 post-mannitol challenge 2. Median difference, p value and 95% CI were provided using the Hodges-Lehmann estimator.
head(blood_p) SUBJID TRT_A TRT_B
1 1 143.670 153.316
2 2 163.082 170.576
3 3 153.393 168.599
4 4 153.082 142.358
5 5 146.720 141.193
6 6 150.668 147.204Results Comparison
Summary and Recommendation
- If you need a flexibility of choosing between methods (exact, non-exact etc) in one software, go for R or StatXact.
- If you need a detailed documentation explaining applied methods, go for StatXact.
- If you only need p value and don’t mind a default exact or t-Student distribution depending on N, you can choose SAS.
- If you need 0s to contribute to the analysis, go for Coin package in R or StatXact.
- If your dataset has ties, go for Coin package in R or StatXact.
Additional References
Details of how to implement the methods in the discussed software are available below:
R:
- Check how to perform this analysis in R here
SAS & StatXact:
- Check how to perform this analysis in SAS & StatXact here