Estimating Cumulative Incidence Functions Using SAS
Objective
In this document we present how to estimate the cumulative incidence function (CIF) in SAS (version 9.4). We focus on the competing risks model where each subject experiences only one out of k possible events as depicted in the figure below.
Data used
The bone marrow transplant (BTM) dataset as presented by Guo & So (2018) is used. The dataset has the following variables:
Grouphas three levels, indicating three disease groups: ALL, AML-Low Risk, AML-High Risk.Tis the disease-free survival time in days. A derived variableTYears = T/365.25is used in the analysis.Statushas value 0 ifTis censored; 1 ifTis time to relapse; 2 ifTis time to death.WaitTimeis the waiting time to transplant in days. This variable is not used here.A new variable
IDis created.
SAS code to prepare the data:
proc format;
value DiseaseGroup 1='ALL'
2='AML-Low Risk'
3='AML-High Risk';
value EventStatus 0='Censored'
1='Relapse'
2='Death';
run;
libname datalib "..\data";
data bmt;
set datalib.bmt;
TYears = T / 365.25;
ID = _n_;
format Group DiseaseGroup.;
format Status EventStatus.;
run;Estimating CIFs in SAS
PROC LIFETEST is used to estimate the CIFs in SAS. For illustration, we model the time to relapse.
ods graphics on;
proc lifetest data=bmt
plots=cif(test)
error=aalen
conftype=loglog
outcif=cif1
timelist=0.5 1 1.5 2 3;
time Tyears * Status(0) / eventcode=1;
strata Group / order=internal;
format Group DiseaseGroup.;
run;
ods graphics off;Below are selected outputs for comparison with the R outputs in the companion document.
CIF estimates for time to relapse at selected timepoints for ‘AML-Low Risk’ patients:
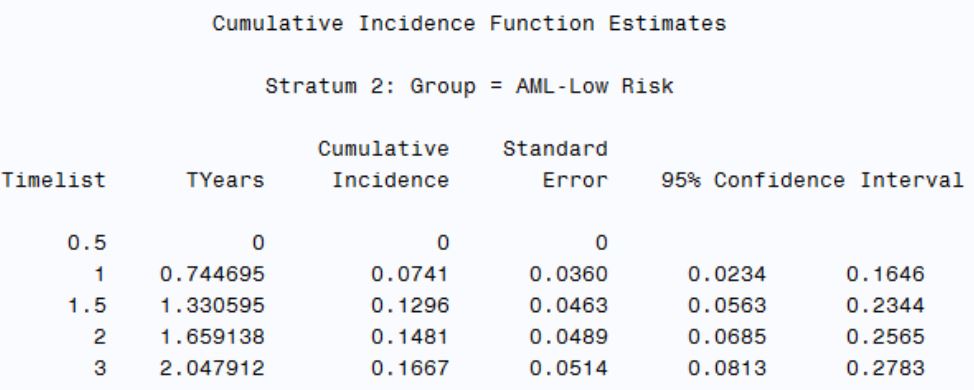
CIF estimates for time to relapses:
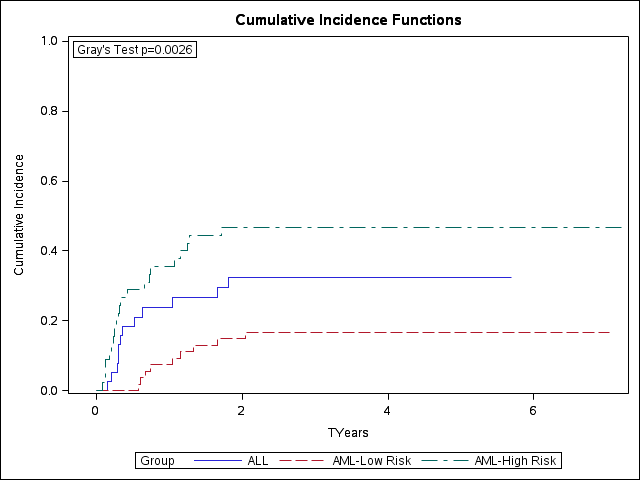
Two points to note:
By default the variance of the estimated CIF are estimated with Aalen’s asymptotic method. This can be changed to the delta method by setting
error=deltain the PROC LIFETEST statement.By default the log-log transformation is used to produce the pointwise confidence intervals (CIs) for the estimated CIFs. To select other methods, for instance log, set
conftype=log.
Reference
Aalen O. (1978). Nonparametric Estimation of Partial Transition Probabilities in Multiple Decrement Models, Annals of Statistics, 6:534-545.
Gray R. (1988). A Class of K-Sample Tests for Comparing the Cumulative Incidence of a Competing Risk, Annals of Statistics, 16:1141-1154.
Gray R. (2024). cmprsk: Subdistribution Analysis of Competing Risks. https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/cmprsk/cmprsk.pdf
Guo C and So Y. (2018). Cause-Specific Analysis of Competing Risks Using the PHREG Procedure. In Proceedings of the SAS Global Forum 2018 Conference. Cary, NC: SAS Institute Inc. https://support.sas.com/resources/papers/proceedings18/2159-2018.pdf.
SAS (2019). Statistical Analysis Software. Users’ Guide Statistics Version 9.4. SAS Institute Inc., Cary.