data read;
input score count @@;
datalines;
40 2 47 2 52 2 26 1 19 2
25 2 35 4 39 1 26 1 48 1
14 2 22 1 42 1 34 2 33 2
18 1 15 1 29 1 41 2 44 1
51 1 43 1 27 2 46 2 28 1
49 1 31 1 28 1 54 1 45 1
;One Sample t-test in SAS
In SAS, a one sample t-test is usually performed using PROC TTEST. The one sample t-test compares the mean of the sample to a provided null hypothesis, called “h0”. The h0 value is provided as an option. By default, the h0 value is zero (0). Running the procedure produces a set of results that suggest whether or not the null hypothesis should be rejected.
Data Used
The following data was used in this example.
Normal Data
By default, SAS PROC TTEST t-test assumes normality in the data and uses a classic Student’s t-test.
Code
The following code was used to test the comparison of a reading scores against a baseline hypothesis value of 30:
proc ttest data=read h0=30;
var score;
run;Output:
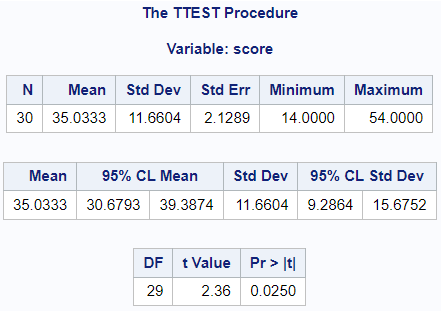
Lognormal Data
The SAS one sample t-test also supports lognormal analysis for a one sample t-test.
Code
Using the same data as above, we will set the “DIST” option to “lognormal” to perform this analysis:
proc ttest data=read h0=30 dist=lognormal;
var score;
run;Output:
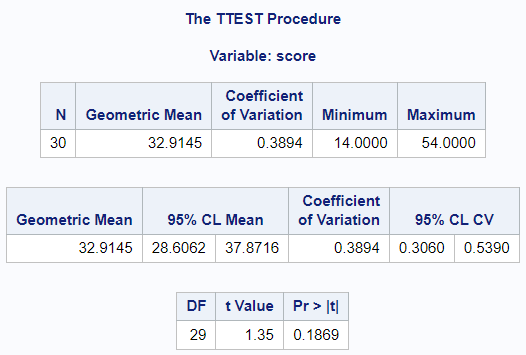
As can be seen in the figure above, the lognormal variation of the one sample TTEST provides results for geometric mean, coefficient of variation, and 95% confidence limits for the coefficient of variation.