Survival Analysis Using SAS
The most commonly used survival analysis methods in clinical trials include:
Kaplan-Meier (KM) estimators: non-parametric statistics utilized for estimating the survival function
Log-rank test: a non-parametric test for comparing the survival functions across two or more groups
Cox proportional hazards (PH) model: a semi-parametric model often used to assess the relationship between the survival time and explanatory variables
Additionally, other methods for analyzing time-to-event data are available, such as:
Parametric survival model
Accelerated failure time model
Competing risk model
Restricted mean survival time
Time-dependent Cox model
While these models may be explored in a separate document, this particular document focuses solely on the three most prevalent methods: KM estimators, log-rank test and Cox PH model.
Analysis of Time-to-event Data
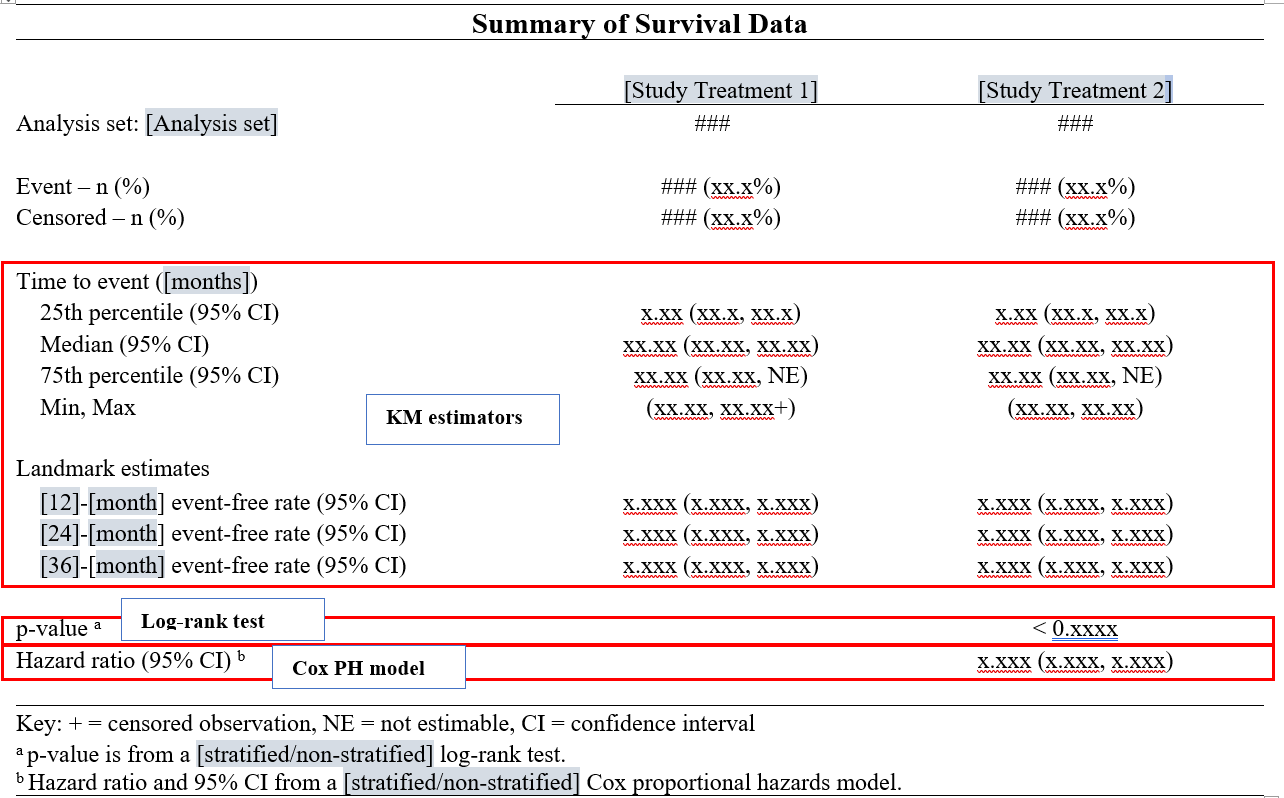
Below is a standard mock-up for survival analysis in clinical trials.
Example Data
Data source: https://stats.idre.ucla.edu/sas/seminars/sas-survival/
The data include 500 subjects from the Worcester Heart Attack Study. This study examined several factors, such as age, gender and BMI, that may influence survival time after heart attack. Follow up time for all participants begins at the time of hospital admission after heart attack and ends with death or loss to follow up (censoring). The variables used here are:
lenfol: length of followup, terminated either by death or censoring - time variable
fstat: loss to followup = 0, death = 1 - censoring variable
afb: atrial fibrillation, no = 0, 1 = yes - explanatory variable
gender: males = 0, females = 1 - stratification factor
libname mylib "..\data";
data dat;
set mylib.whas500;
lenfoly = round(lenfol/365.25, 0.01); /* change follow-up days to years for better visualization*/
run;The Non-stratified Model
First we try a non-stratified analysis following the mock-up above to describe the association between survival time and afb (atrial fibrillation).
The KM estimators and log-rank test are from PROC LIFETEST, and Cox PH model is conducted using PROC PHREG.
KM estimators and log-rank test
proc lifetest data=dat outsurv=_SurvEst timelist= 1 3 5 reduceout stderr;
time lenfoly*fstat(0);
strata afb;
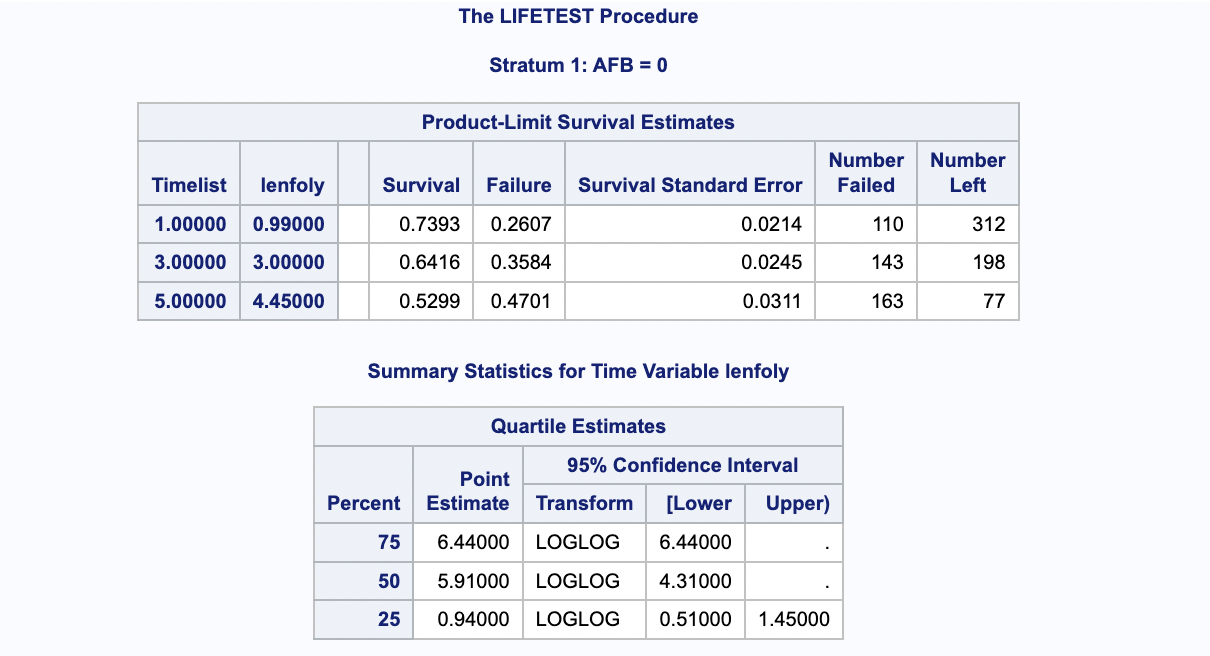
run;The landmark estimates and quartile estimates for AFB = 0 group are as shown in below:
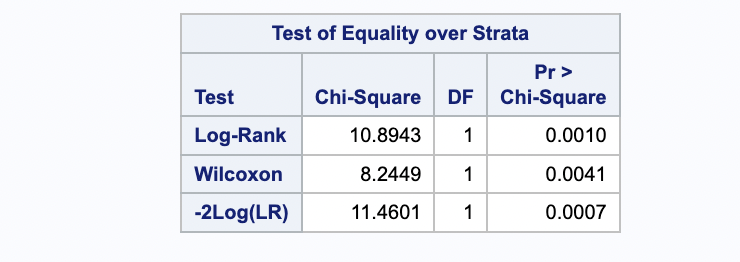
The logrank test result is in below:
Cox PH model
proc phreg data = dat;
class afb;
model lenfol*fstat(0) = afb/rl;
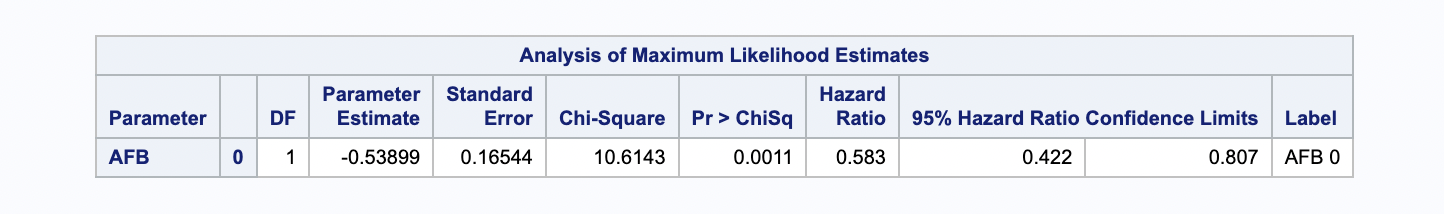
run;The hazard ratio and confidence intervals are shown as below:
The Stratified Model
In a stratified model, the Kaplan-Meier estimators remain the same as those in the non-stratified model. To implement stratified log-rank tests and Cox proportional hazards models, simply add the STRATA option in both PROC LIFETEST and PROC PHREG.
# KM estimators and log-rank test
proc lifetest data=dat;
time lenfoly*fstat(0);
strata gender/group = afb;
run;
# Cox PH model
proc phreg data=dat;
class afb;
model lenfol*fstat(0) = afb/rl;
strata gender;
run;