data pressure;
input SBPbefore SBPafter @@;
datalines;
120 128 124 131 130 131 118 127
140 132 128 125 140 141 135 137
126 118 130 132 126 129 127 135
;Paired t-test
Paired t-test in SAS
The Paired t-test is used when two samples are naturally correlated. In the Paired t-test, the difference of the means between the two samples is compared to a given number that represents the null hypothesis. For a Paired t-test, the number of observations in each sample must be equal.
In SAS, a Paired t-test is typically performed using PROC TTEST.
Normal Data
By default, SAS PROC TTEST t-test assumes normality in the data and uses a classic Student’s t-test.
Data Used
The following data was used in this example.
Code
The following code was used to test the comparison of two paired samples of Systolic Blood Pressure before and after a procedure.
proc ttest data=pressure;
paired SBPbefore*SBPafter;
run;Output:
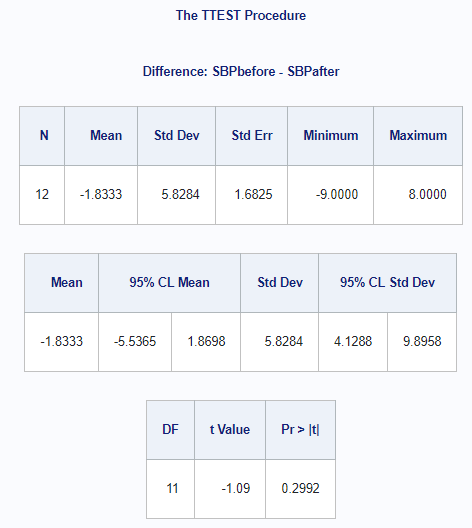
Lognormal Data
The SAS paired t-test also supports analysis of lognormal data. Here is the data used for the lognormal analysis.
Data
data auc;
input TestAUC RefAUC @@;
datalines;
103.4 90.11 59.92 77.71 68.17 77.71 94.54 97.51
69.48 58.21 72.17 101.3 74.37 79.84 84.44 96.06
96.74 89.30 94.26 97.22 48.52 61.62 95.68 85.80
;Code
For cases when the data is lognormal, SAS offers the “DIST” option to chose between a normal and lognormal distribution. The procedure also offers the TOST option to specify the equivalence bounds.
proc ttest data=auc dist=lognormal tost(0.8, 1.25);
paired TestAUC*RefAUC;
run;Output:
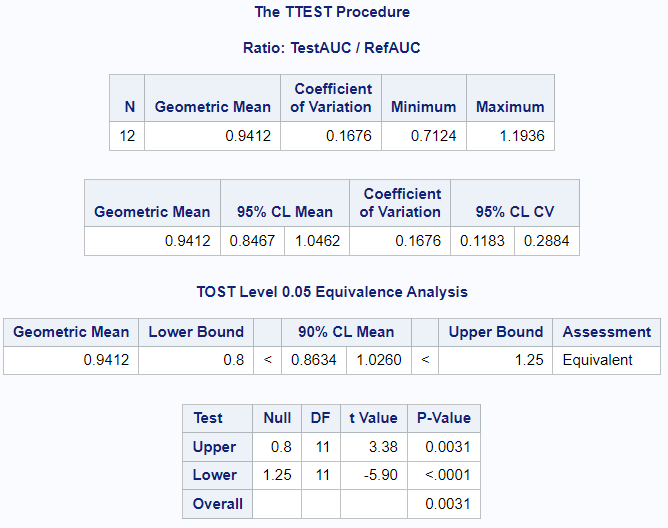
As can be seen in the figure above, the lognormal variation of the TTEST procedure offers additional results for geometric mean, coefficient of variation, and TOST equivalence analysis. The output also includes multiple p-values.